With the development of IT technologies and their introduction into people’s daily lives, the importance of data has reached a new level. The best computer engineers have developed RAID technology, which the main purpose is to prevent data loss, but as practice shows, even RAID arrays can break. In this article, we will look at the main causes of RAID 3 and RAID 4 failures and ways to recover lost data.

Contents
- How RAID 3 and RAID4 works?
- The difference between RAID 3 and RAID4
- The main reasons for data loss on RAID 3 and RAID 4 arrays
- How to recover lost data if a RAID 3 or RAID 4 array fails?
How RAID 3 and RAID4 works?
If you want to build a third or fourth level RAID array you will need at least three disks. This requirement is due to the principle of how the array works. The reason is that RAID 3 and RAID 4 use striping technology (just like RAID 0) plus a third disk is dedicated specifically to storing parity data. The parity value is automatically calculated while writing the information to the disks and written to the allocated drive. This value is further used during data transfer (move or copy) and allows to check the integrity of the information. In case of errors, exclusive information for each disk is calculated to recover the lost information.
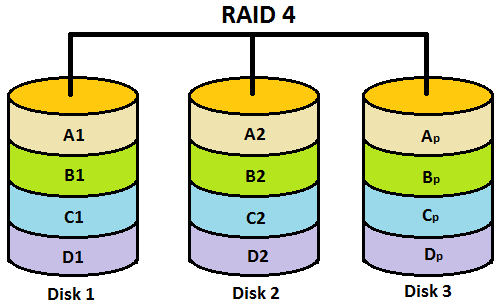
It is worth noting that the speed with this arrangement will be noticeably faster than with RAID 1 and in case of one disk failure the array will continue to work. The user will see the corresponding message only and will notice the performance degradation. In this case, the failed disk should be replaced immediately, otherwise, information might be lost.
If we compare RAID 0 (Striping) to RAID 3 or RAID 4 the performance of the latter two will be significantly slower since it takes time to write the checksum to the third disk.
It should not be forgotten that RAID 3 and RAID 4 are not very widespread and are rarely used today due to the very slow performance of multiple simultaneous requests for information. The reason is that the information is read/written across all drives at the same time while the parity data is stored on one dedicated disk only so it is physically impossible to achieve the needed performance. Therefore, RAID 3 and RAID 4 are best used, for example, for video storing, streaming, etc., where there is a long transfer of information with a minimum number of I/O requests.
The difference between RAID 3 and RAID4
RAID 3 and RAID 4 are very similar. They have the same structure and the minimum number of disks needed for normal operation. Both of these arrays use a dedicated disk to write parity data, which is used to recover lost data if needed. The main difference is the size of the minimum block of information that is written to the disks. RAID 4 divides data into blocks rather than bytes (as in RAID 3). This partially solves the problem of low write speeds with simultaneous I/O requests. However, because the parity calculation and its writing to a separate disk is a weakness, today RAID 3 and RAID 4 are seldom used due to the availability of faster RAID levels which allow a high level of data protection without performance degradation. You can read the article “RAID types – which type is best to choose?” for more details.
The main reasons for data loss on RAID 3 and RAID 4 arrays
RAID arrays allow to ensure data integrity in case of a drive failure, but apart from this, there are many other reasons why users can lose important information. For example, the main enemy of RAID arrays (as well as any technology in principle) is power surges, which can cause several drives to fail at the same time. In this situation, it is quite difficult to recover the lost data, since first of all, it is necessary to replace the failed parts for each drive and only then proceed directly to data recovery. In addition, the controller (both hardware and software) is especially sensitive to sudden power outages or voltage drops. As it is responsible for the distribution of information between the drives, even if it is replaced by an identical one, it is not always possible to restore the array performance. The thing is that the new controller will not be able to determine where the initial block of information is located and therefore will not be able to build the array correctly. Therefore, when creating a RAID array of any level, first of all, take care of an uninterrupted power supply, which will help to avoid many problems in the future.
Among the most common causes of RAID 3 and RAID 4 failures are array rebuild errors after a system reboot. Usually, the controller cannot rebuild the array because there are too many bad sectors that cause errors during array rebuilding, drives are connected incorrectly (often after service maintenance), or the connection cables are damaged.
Human error is one more reason for the loss of important information. Even if everything is set up correctly and the array is working as it should be, you can not exclude the possibility of accidental file deletion, partition formatting, or improper data manipulation, etc. In this case, you will have to use data recovery software. The best option would be to use RS RAID Retrieve since it is very easy to use and allows you to recover lost data in the most complicated situations.
Operating system failures can also affect the functionality of RAID 3 and RAID 4. This is especially true for RAID arrays that are based on a software controller, as the functionality of the RAID array is directly dependent on the operating system, and if it fails you will almost certainly receive an inoperable RAID array. Hardware controllers are less dependent on the operating system, but their price is noticeably higher, while the software RAID array can be built in almost any operating system. For information on how to build software RAID, you can read the article “Software RAID – Advantages and Drawbacks“
RAID can be broken by viruses or adware. A virus can not only delete, damage, or make the files unreadable but also damage the logical disk structure, which in turn greatly affects the array performance or startup. Therefore it is strongly recommended to check the array regularly for the presence of malware. Both paid and free solutions can be used.
And finally, it is impossible not to mention failures in the logical structure of drives. They can occur for various reasons, for example, either due to errors in the controller or due to a large number of bad blocks on the drive. In either case, your RAID 3 or RAID 4 array will either start to slow down and give you a disk failure notification, or it will stop running altogether. So we strongly recommend that you use only high-quality components that you can be 100% sure will work.
How to recover lost data if a RAID 3 or RAID 4 array fails?
RAID 3 and RAID 4 performance depends largely on the degree of maintenance (analyzing the health of the drives, removing junk for good performance, fixing software bugs, etc.). However, even with proper maintenance, unexpected situations do occur. Especially when users delete data they do not need, but later it turns out that the data is needed and must be recovered. Whatever the cause of data loss, it is important to know how to act correctly, firstly, to avoid damaging the information on the disks, and secondly: to ensure the highest probability of successful data recovery.
The first thing to do is to extract the data from the RAID 3 or RAID 4 array and only then proceed to restore the array.
To do this you should:
Step 1: Download and install RS RAID Retrieve. Launch the application after installing. The built-in “RAID constructor” will open in front of you. Click “Next“
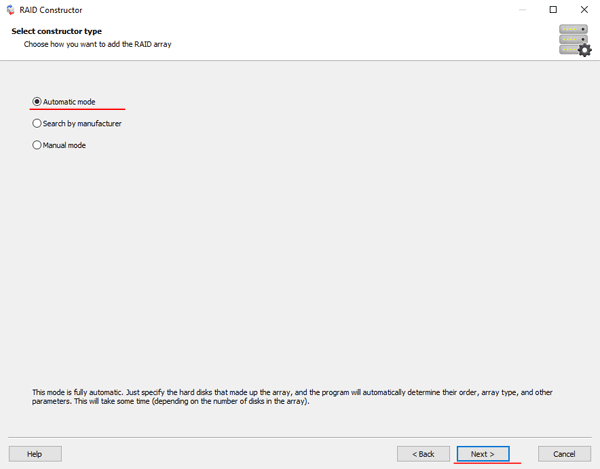
Step 2: Choose the method of adding a RAID array for scanning. RS RAID Retrieve offers three options to choose from:
- Automatic mode – allows you to simply specify the drives that made up the array, and the program will automatically determine their order, array type, and other parameters;
- Search by manufacturer – this option should be chosen if you know the manufacturer of your RAID controller. This option is also automatic and does not require any knowledge about the RAID array structure. Having the manufacturer’s information allows you to reduce the time to build the array, and is, therefore, faster than the previous option;
- Manual creation – this option is worth using if you know what type of RAID you are using. In this case, you can specify all parameters you know, and those which you do not know – the program will automatically determine
After you select the appropriate option – click “Next“.
Step 3: Select the disks that make up the RAID array and click “Next“. It will start the process of detecting the array configurations. When it is complete, click “Finish“.
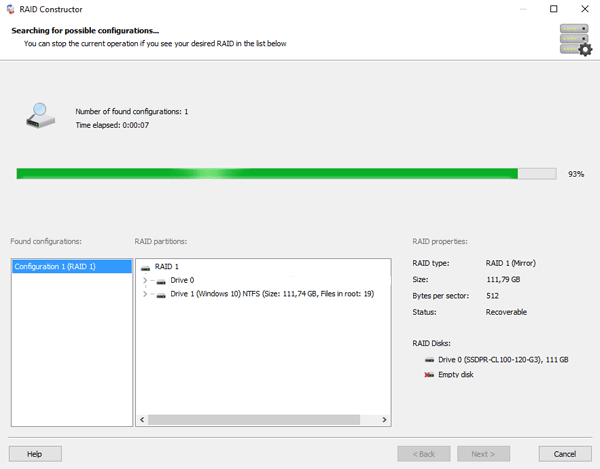
Step 4: After the constructor builds the array – it will appear as a regular drive. Double left-click on it. The File Recovery Wizard will open in front of you. Click “Next“
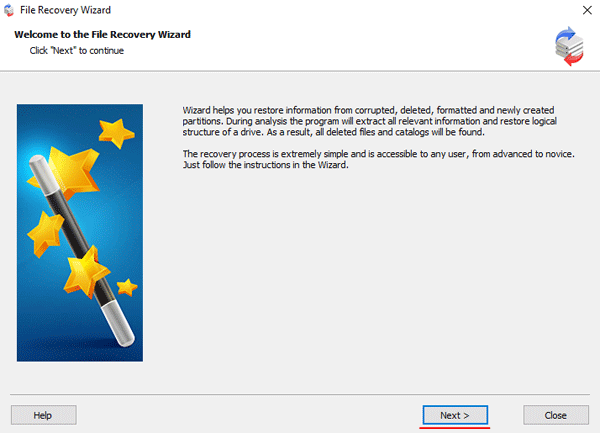
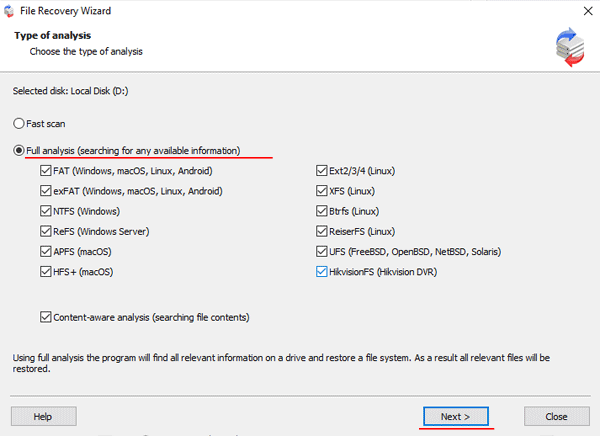
Step 5: RS RAID Retrieve will offer to scan your array for files to recover. You will have two options: a quick scan and a full analysis of the array. Select the desired option. Then select the file system type that was used on the array. If you do not know this information, check all available options, like on the screenshot. It is worth noting that RS RAID Retrieve supports ALL modern file systems.
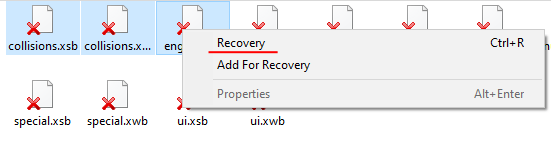
Step 6: The array scanning process will start. When it finishes, you will see the previous structure of files and folders. Find the necessary files, right-click on them and select “Recovery“
Step 7: Specify the location where the recovered files will be saved. This can be a hard drive, a ZIP-archive, or an FTP-server. Click “Next“
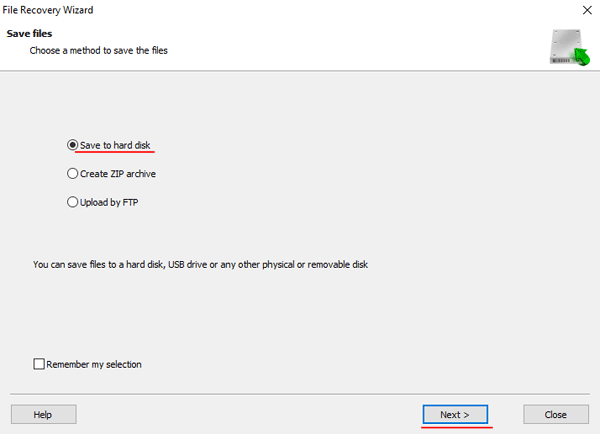
After clicking the “Next” button, the program will begin the recovery process. When it finishes – the selected files will be in the specified location.
After all, files are successfully restored – recreate the RAID 3 or RAID 4 array, and then copy the files back.
As you can see, the data recovery from RAID 3 and RAID 4 arrays is quite simple and doesn’t require much PC knowledge, making RS RAID Retrieve the perfect application for professionals and novice users alike.











