In this article, we will learn how to convert a dynamic foreign disk to a basic disk in the Windows operating system.

Contents
- What is dynamic disk in Windows?
- Advantages and disadvantages of using dynamic disks
- How to convert a basic disk to dynamic using Disk Management?
- How to convert a basic disk to dynamic using the command prompt or "Windows PowerShell"?
- What kind of operations can be performed with dynamic disks?
- Why does the drive appear as a "Dynamic Foreign drive" in Windows?
- How to convert Dynamic Foreign Disk into basic one without data loss?
What is dynamic disk in Windows?
Windows Dynamic Disks is a Microsoft proprietary technology that allows you to combine several physical disks into a single logical volume, create logical volumes from parts of different disks, or create logical volumes that are larger than the whole size of one disk (using free disk space from a different disk).
To better understand how dynamic disks work, let’s imagine two 100 GB disks each. If we need to create a partition of 120 GB, when they are basic disks — we will not be able to do that, since we are limited by the physical size of the drive. However, if we convert these disks to dynamic, we get 200 GB (2 x 100 GB) of memory which we can partition however we want. For example, we can now create a 120 GB logical volume, since we are no longer limited to the disc space of a single drive, but an entire group of dynamic drives. Schematically, it can be shown as follows:
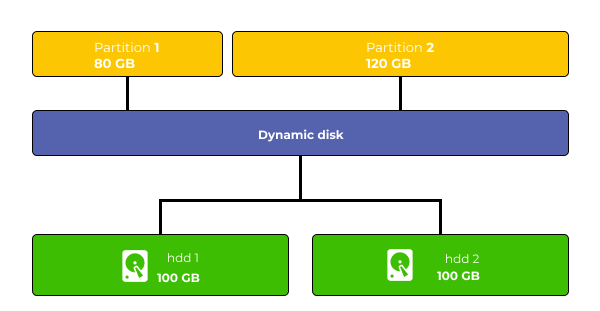
As a different example, we can imagine again two disks 100 GB each (2 x 100 GB = 200 GB), but the first disk has 50 GB free space and the second 25 GB. If the disks are dynamic, we can easily combine the free disk space into a single volume, obtaining 75 GB of memory. The result would be following: first one — 50GB, second — 75GB , and third — 75GB (50GB + 75GB + 75GB = 200 GB). That is, as mentioned above – the user allocates the total disk space, not the space of a single disk.
It is also worth noting that the same technology (dynamic disks) is used in Windows to create software RAID arrays but in a little modified form. You can read about what are RAID arrays in the article “What are RAID arrays – types and how to use them?“
The Linux operating system has some analog of dynamic disks called LVM (Logical Volume Manager). More information about LVM can be found in the article “Comparison and difference between RAID lvm and mdadm“
Advantages and disadvantages of using dynamic disks
The Windows operating system works with all disks by default as basic. However, you always have the option of converting any drive to dynamic using the operating system’s built-in capabilities.
But before using dynamic disks, it is important to understand their advantages and disadvantages compared to basic disks. Thus the user will know what he will face when using dynamic disks, and therefore the choice to use or not to use this technology will be more informed.
The main advantages of dynamic disks are following:
- the ability to create volumes that are larger than the physical size of a single disk;
- the ability to combine memory blocks located on different physical disks into a single volume;
- the ability to flexibly change the size of a disk partition (for example, you can connect an additional disk and add its space to an existing dynamic disk);
Although dynamic disks are incredibly flexible in their use of disk space, they also have disadvantages:
- it is impossible to install multiple operating systems on dynamic disks. If you try to install a second operating system on a dynamic disk, you will see a message stating that you must convert the disk to a basic one;it is impossible to install multiple operating systems on dynamic disks. If you try to install a second operating system on a dynamic disk, you will see a message stating that you must convert the disk to a basic one;
- you cannot access dynamic disks on older Windows versions. Support for dynamic disks begins with Windows Vista and later;
- if a partition is mounted on two physical disks, all information is lost if either disk fails;
- if you move a dynamic disk to a different computer, you must connect all the drives that make up a dynamic disk to that computer. Otherwise, the information will be unavailable;
- if the dynamic disk is located on several physical disks — the speed will be noticeably slower than on the basic disks. This is due to the peculiarities of request scheduling;
- if you make a system disk dynamic – you will automatically lose the possibility to update or reinstall the operating system since the Windows installer doesn’t know how to work with them;
- Home versions of Windows do not know how to work with dynamic disks;
As you can see, dynamic disks have a lot of disadvantages too. So before you use this technology, you should think it over carefully. It will allow you to avoid many problems in the future.
How to convert a basic disk to dynamic using Disk Management?
If you have analyzed all the advantages and disadvantages of dynamic disks and decided to use them – you can convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk in almost a few steps:
Step 1: Right-click on “Start” and choose “Run“. The same operation can be performed using the “Win + R” key combination
Step 2: In the window that opens, type the command “diskmgmt.msc” and press “Enter” to confirm.
A system utility called “Disk Management” will open in front of you. In the “Type” column, next to each disk, you will see the disk type – dynamic or basic.
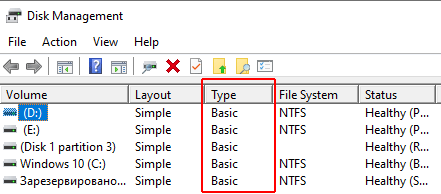
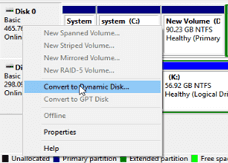
Step 3: Right-click on the square of the disk you want to convert, and choose “Convert to Dynamic Disk…“
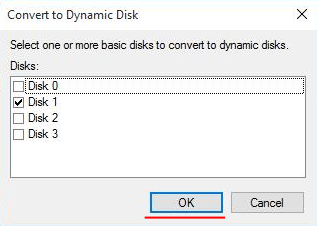
Step 4: Select the drives that will make up your new dynamic disk and click “OK“
After clicking “OK” the selected disks will be converted to dynamic, and now you can allocate the disk space as you want.
How to convert a basic disk to dynamic using the command prompt or “Windows PowerShell”?
You can also use the command prompt or Windows PowerShell to convert basic disks into dynamic.
It is worth noting that the entire conversion procedure consists of several commands, so even if you are not familiar with the command prompt, you will have no problems converting basic disk into dynamic.
So, in order to convert a basic disk into dynamic you should:
Step 1: Right-click on “Start” and select the “Windows PowerShell (admin)“
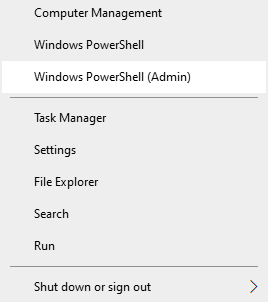
Step 2: You will see the Windows PowerShell window. Run the following commands (pressing “Enter” after each command to execute):
- diskpart – this command launches the diskpart utility, which is used to work with disks;
- list disk – to display the disks connected to the computer;
- select disk N – this command selects the disk for further work. Replace N with the number of the disk to be converted to dynamic;
- convert dynamic – to convert the selected disk into dynamic;
- exit – to exit the diskpart utility;
These commands should be performed for all disks you wish to convert to dynamic.
What kind of operations can be performed with dynamic disks?
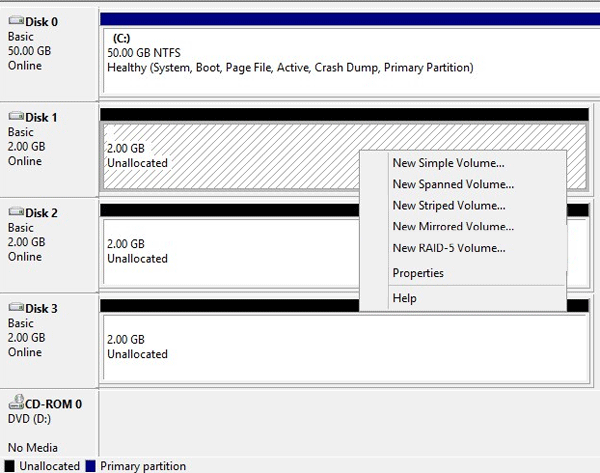
Once you have converted the desired disks to dynamic — you need to decide what to do with them next. Right-click on the dynamic disk you want to work with. You will see the following options:
- New Simple Volume – this command creates the regular volume. Most often simple volume is created to use the disk space that is left after the RAID array creation;
- New Spanned Volume – this option will create a regular JBOD. That is, several disks will be combined into one partition without any resistance;
- New Striped Volume – use this option if you want to create a RAID 0 array. Data in such an array will be written simultaneously on all selected disks. There is no resiliency. For more details see the article “RAID 0 advantages and disadvantages“;
- New Mirrored Volume – this option will create a software RAID 1 array. That is, each of the selected disks will store a copy of all recorded information. For more details you can read the article “RAID 1 how to create, advantages and disadvantages“;
- New RAID-5 Volume — is software RAID 5. That is, it uses striping technology, plus parity data is calculated for each of the disks, which is used in case of a drive failure. More information about RAID 5 you can find in the article “How to create a software RAID 5“;
The following steps look the same no matter which option you choose:
Step 1: The Disk Wizard will open in front of you. We have selected “New Simple Volume“, therefore the “New Simple Volume Wizard” will open in front of us. Click on “Next“
Step 2: Specify the size of the future volume. By default, the system will automatically set the maximum available size. Click “Next“
tep 3: Assign a drive letter. You can choose from the list, or you can leave the one that the system suggests. After that click “Next” again.
Step 4: Choose a file system type. By default, Windows suggests using NTFS. Click “Next“
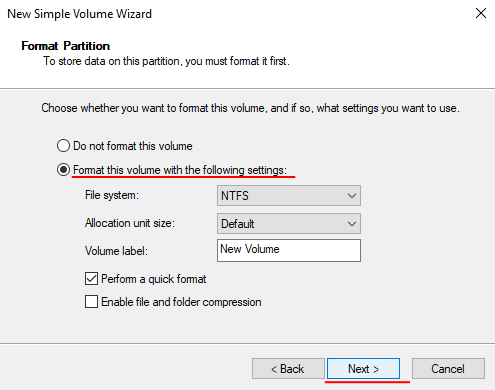
Step 5: Now, all you have to do is check the parameters of your future dynamic drive. If everything is okay, click “Finish“
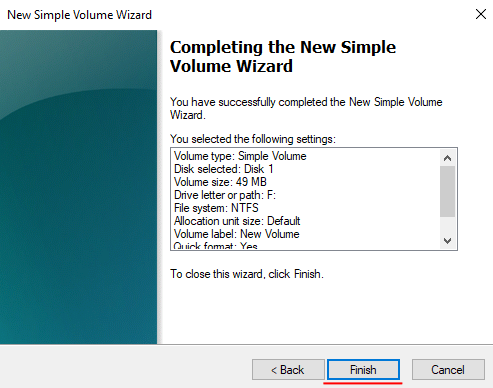
After that, your dynamic disk will be created. It will be displayed in Windows Explorer, and you will be able to perform the same operations with it as with a regular disc.
Why does the drive appear as a “Dynamic Foreign drive” in Windows?
Quite often users may observe a situation when a drive stops appearing in Explorer, and in Disk Management it appears as “Dynamic, Foreign“. Most often this happens after installing a second operating system or reinstalling Windows. Slightly less often it occurs after servicing the computer.
In the first two cases, the reason is that the new system does not know how to work with a dynamic array correctly. That is because dynamic disks are created by the means of the operating system, which remembers how to work with them. The new system will not have information, for example, on what disk is the initial block from which to start reading the information, the order of the drives in a dynamic disk or RAID array, etc.
In the third case, the cause may be a weak connection cable (if, of course, there was hardware maintenance (dusting, changing thermal paste, etc.), but not the software).
It is also worth noting that if the drive was working properly in the operating system, and suddenly it displays as “foreign” – the reason may be a physical failure. In such a situation it is recommended to listen for any unusual noises (clunking, crackling, etc.). You can also check the drive for bad sectors. For information on how to do this, read the article: “How to check and fix errors on a hard disk or SSD drive?“
You can try to import a foreign dynamic disk into your operating system, but in this case, you might lose data. Therefore, if there is no important information on it, follow a series of simple steps:
Step 1: Right-click on “Start” and select “Disk Management“
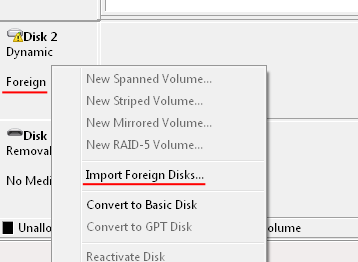
Step 2: The Disk Management utility window will open in front of you. Find the drive you want to convert into a basic one, right-click on it, and choose “Import Foreign Disks…“
It will open a list of all the disks included in the dynamic drive that will be imported into the system. Check if all the disks you want are selected and click “OK“
After that, the disk importing will start, and upon its completion, the drives will be displayed in Windows Explorer. Their status will be shown in the Disk Management Utility as “Healthy“
Unfortunately, the above operation is not always successful. In such a situation, it is better to try to convert the disk back to a basic one. But here, you should remember that all data on the disks will be destroyed.
So, to convert a dynamic disk into a basic one, repeat the first two steps described above, but instead of “Import Foreign Disks…” choose “Convert to Basic Disk“
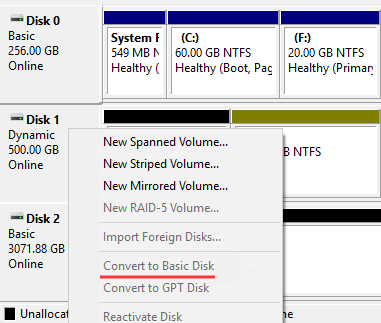
Now all drives, included in the dynamic disk, will be converted to basic ones.
If this option does not work either, you can connect each disk individually and choose “Delete Volume“
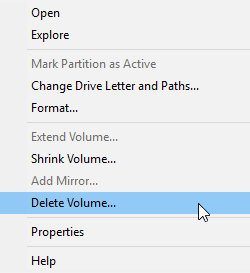
All data on the volume will be deleted, and then it will become basic again.
How to convert Dynamic Foreign Disk into basic one without data loss?
All of the methods described above for converting a dynamic disk into a basic one lead to data loss in one way or another. But what to do if a dynamic disk stores data worth thousands of dollars or specific importance to its owner, and suddenly the operating system stops working, or after reinstalling the system the disk shows up as “Dynamic, Foreign“?
In such a situation, under no circumstances convert it to basic and do not try to import it, as the probability of data loss is very high.
The best thing to do is to use RS RAID Retrieve — the best RAID reconstructor that knows how to extract the data from dynamic disks.
The program has an intuitive interface, so you don’t need to have in-depth PC knowledge to successfully extract the data from a “Dynamic Foreign Drive”
Moreover, the built-in RAID constructor can automatically detect all dynamic disk parameters, such as the RAID type that was used, the initial block to read, the order of the disks, etc.
All you need to do is a few clicks of the mouse.
So, in order to extract the data from a dynamic foreign disk, first, connect all the drives that make up the dynamic disk to your computer and then follow a few simple steps:
Step 1: Download and install RS RAID Retrieve.

Data recovery from damaged RAID arrays
Launch the application after installing. The built-in “RAID constructor” will open in front of you. Click “Next“
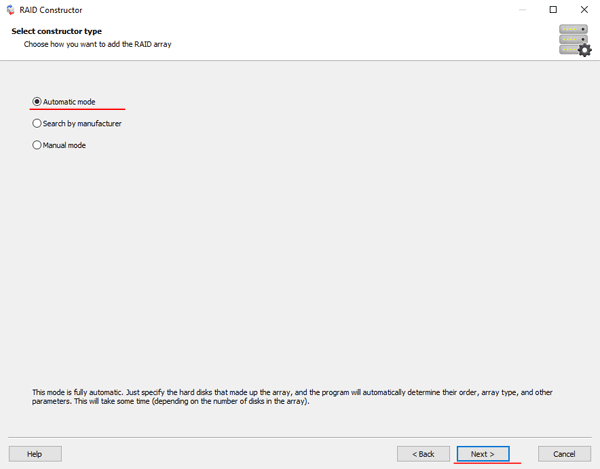
Step 2: Choose the method of adding a dynamic disk for scanning. RS RAID Retrieve offers three options to choose from:
- Automatic mode – allows you to simply specify the drives that made up the array, and the program will automatically determine their order, array type, and other parameters;
- Search by manufacturer – this option should be chosen if you know the manufacturer of your RAID controller. This option is also automatic and does not require any knowledge about the RAID array structure. Having the manufacturer’s information allows you to reduce the time to build the array, and is, therefore, faster than the previous option;
- Manual creation – this option is worth using if you know what type of RAID you are using. In this case, you can specify all parameters you know, and those which you do not know – the program will automatically determine
After you select the appropriate option – click “Next“.
Step 3: Select the drives that make up your dynamic disk and click “Next“. It will start the process of detecting the correct configurations. When it is complete, click “Finish“.
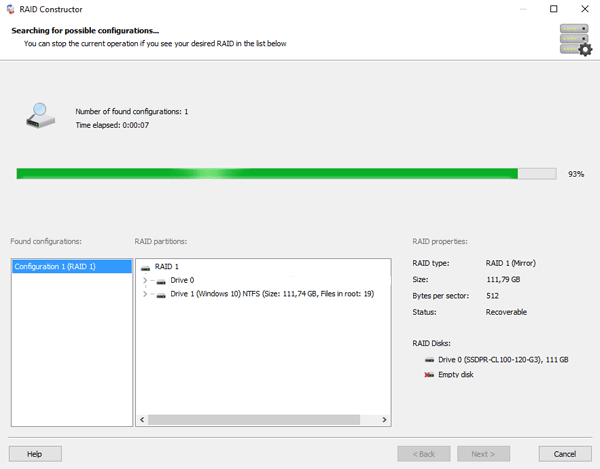
Step 4: After the constructor builds the dynamic disk – it will appear as a regular drive. Double left-click on it. The File Recovery Wizard will open in front of you. Click “Next“
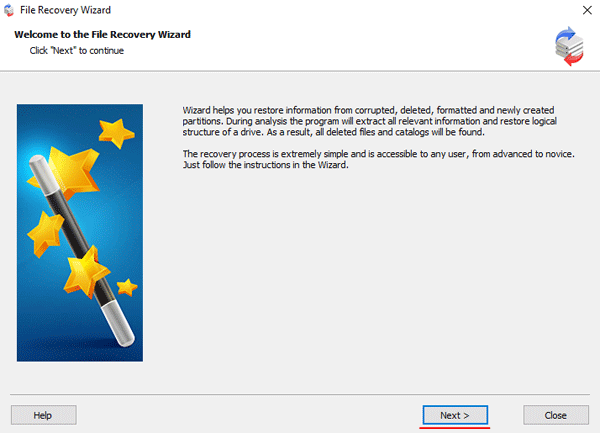
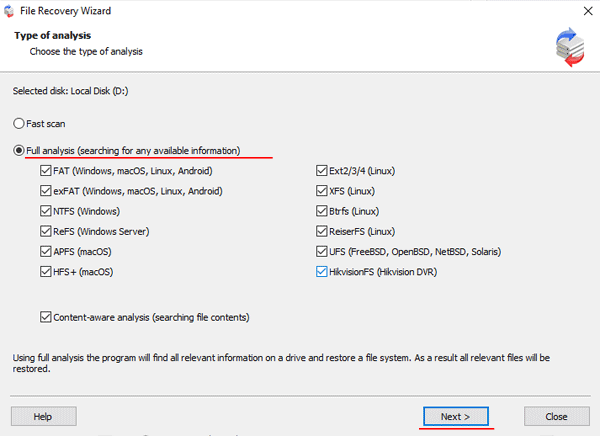
Step 5: RS RAID Retrieve will offer to scan your disk for files to recover. You will have two options: a quick scan and a full analysis of the array. Select the desired option. Then select the file system type that was used. If you do not know this information, check all available options, like on the screenshot. It is worth noting that RS RAID Retrieve supports ALL modern file systems.
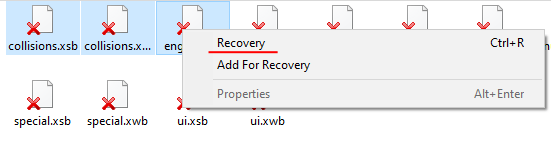
Step 6: The dynamic disk scanning process will start. When it finishes, you will see the previous structure of files and folders. Find the necessary files, right-click on them and select “Recovery“
Step 7: Specify the location where the recovered files will be saved. This can be a hard drive, a ZIP-archive, or an FTP-server. Click “Next“
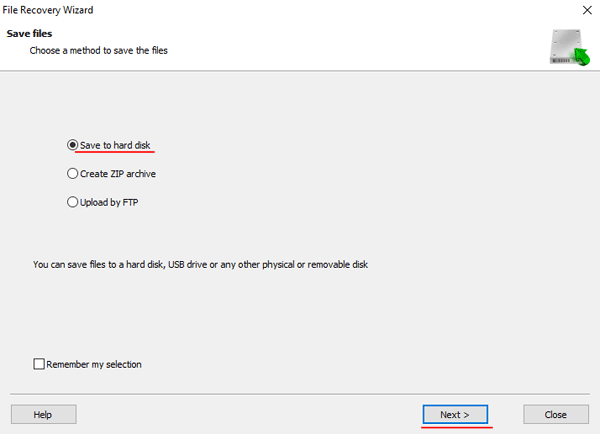
After clicking the “Next” button, the program will begin the recovery process. When it finishes – the selected files will be in the specified location.
Once the data is in a safe place you can convert your dynamic disk to a basic one by using any of the methods described in the previous paragraph of this article.