In today’s world, a large number of devices use memory cards to expand their storage capacity. With the advent of high-definition video formats such as 4k, there are certain requirements for memory cards to be able to record data at a certain speed. In this article, we will show you how to choose the right memory card for your device.

Contents
- Memory card size: SD, miniSD, and microSD
- Memory card capacities
- Memory card speed classes
- UHS-I and UHS-II - what's the advantage?
- Memory card file systems
- Write protection for memory cards
- SD express PCIe -- the future of SD memory cards
- What should you do if you accidentally format your memory card or lose important data?
Today it is hard to imagine anyone who has never used a smartphone, digital camera, camcorder, mp3 player or book reader. All of these devices use an SD memory card to store data. So, what is SD?
SD (Secure Digital) is the standard for memory cards for electric devices, the main advantage of which is its flexibility, because thanks to the unified standard it can be used with almost any digital device, saving the user from having to buy adapters, converters and other memory card, readers. Want to transfer your data to a PC or notebook? No problem. Just plug your cards out of your digital camera or other gadgets, and put them into your computer’s card reader. It’s simple and straightforward.
At the same time, the SD standard, despite its advantages, has many points that can be a little confusing for you. For example, how do you know whether 32 GB SDHC Class 4 60x Speed Flash Memory Card will work in your camera.
And why buy the $100 memory card shown in the picture below when you can buy a cheaper class memory card for up to half the price? It’s not so much the brand name, as the memory card performance.

Fortunately, there is a certain logic in the name of the memory card. The name is controlled by the SD Association, whose main task is to standardize classes. It was created in 2000 when the three biggest manufacturers (Panasonic, SanDisk, and Toshiba) joined together to set industry standards. This was done so digital devices would know how to work with a certain type of memory card, so you could choose the right card based on the information on the card body.
In theory, it looks a bit complicated, but as practice shows, the user only needs to know three things about his memory card: its physical size, memory capacity, and the data transfer rate.
Memory card size: SD, miniSD, and microSD
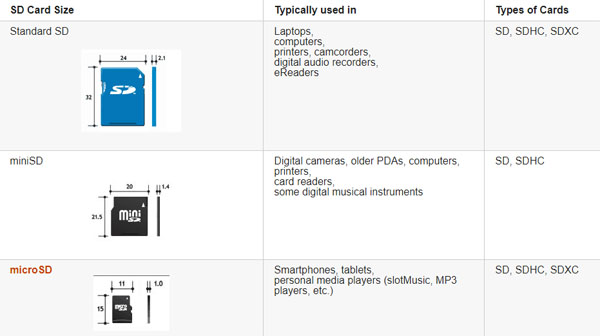
The first thing you should start with when choosing a memory card is the size of the card. Today, all memory cards use three sizes. SD, miniSD, and microSD. But there are also non-standard cards – usually, it is shown on the front of the card.
SD cards are usually used in desktop computers, notebooks, digital camcorders, DVD players, e-book readers, etc.
Below are the sizes of memory cards, as well as the devices that commonly use them.
Of course, the size of SD, miniSD, and microSD cards has created a compatibility problem. After all, it’s difficult to insert a small microSD card into a slot designed for SD cards. This problem was partially solved by the use of special adapters. Usually, when you buy a microSD card, one of these adapters will be available.

There is no backward compatibility (i.e. you cannot fit the SD card into the small microSD slot), so lately users are increasingly choosing the microSD+SD adapter (as shown above) instead of the normal SD card, to get the maximum range of devices on which the memory card can be used.
Memory card capacities
There are three types of SD cards on the market today:
- SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity) or just SD. Capacities of 2 GB or more are available;
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) are larger capacity cards. These cards support up to 32GB;
- SDXC (Secure Digital eXtended Capacity) are high-capacity cards (from 32GB to 2TB);
The capacity of the memory card is usually indicated on the front of the card. Therefore, you do not need to know the capacity range for each type of card by heart. The only important thing to know is whether your device will work with the type of memory card you want to buy, because older gadgets may not support new types of cards, such as SDXC.
That is why, when choosing a memory card, look for the largest compatible card you can find.
One thing you should also be aware of is that SDHC and SDXC are compatible with each other. It means you can use an SDHC card in a device that supports the high-capacity SDXC card, but not vice versa.
To find out which type of memory card your device supports, look at the label on the device (SDXC or SDHC near the memory slot). If you can’t find the supported cards, you can either read your card’s manual or check the manufacturer’s website.
Memory card speed classes
Before discussing the classes of memory cards, it is worth saying that MB/s (or MBps) is usually used to determine how fast data can be written.
Each memory class supports a certain minimum speed and has its logo for quick visual identification of the memory class. Below is a list of all memory classes and their specifications:
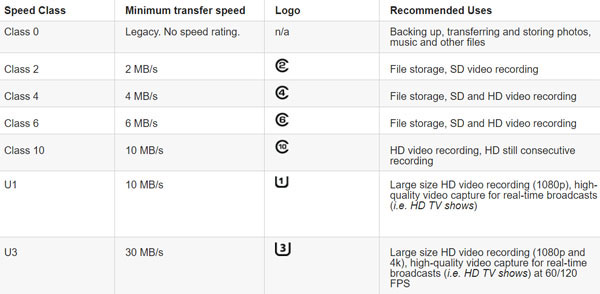
The frequent use of memory cards in camcorders and digital cameras has led to the introduction of Speed Class “V”, which indicates the speed with which these devices work. In 2016, the SD Association introduced a new speed class, which covers both the high-speed bus and the ultra-high-speed bus (UHS) and is designed for HD videos from 720p up to 8K.
The V6 is the same speed as the Class 6 and the V10 is the same speed as the Class 10, but to receive the Vx logo, the card, and the host must support the latest MLC NAND Flash technology and other requirements suitable for video recording.
Below are the specifications for each “V” speed class:

Usually the manufacturer does not know which device will be used with his product. Therefore, the speed class can be written on the front side, and the user will have to decide which one he wants. We recommend that you use the maximum memory card class that your device can support.

It is also worth noting that “X speed classes” were also used in the past. For example, on the front of the memory card, you could see “600x“. This way of displaying speed was invented in the days of CDs. For example, X equals 150kB/s, so 600x equals 90MB/s (600 x 150kB/s = 90,000kB/s).
The problem with this classifying method is that 600x is the manufacturer’s speed and has not been verified or standardized. That is why the SD Association came about, standardizing the speed classes of memory cards, so that each memory card if it has a speed class written on it, must match that class.
It is also worth noting that the speed class usually refers to the slowest data transfer speed, and usually it is the speed at which the memory card is written, as the read speed is usually much faster. Here lies the biggest advantage of the speed ratings from the SD Association, because the X classification usually indicates the maximum speed, which means the speed at which data can be written to the memory cards is often much slower than what is shown label. If the same happens to a class 10 SD card, for example, the SD Association will penalize the dishonest card manufacturer.
UHS-I and UHS-II – what’s the advantage?
As you may have understood from the previous paragraph of this article, today the highest speed class is 10. However, the class 10 memory card is not the fastest flash drive sold in stores.
In addition to the standard set of speed classes, there is also one class, called UHS.
Although Speed Class 10 is the highest in the range, it is not the fastest SD card you can buy. Aside from the standard Speed Class set for SD cards, there is also a class known as UHS Speed Class. There are three different buses for SD cards. The bus is the interface through which devices read and write data from the card. You can choose between a normal bus (slow speed), a high-speed bus, or an ultra-high-speed bus. Cards with the normal and high-speed bus are in the normal speed classes. Cards with an ultra-high-speed bus are UHS speed class cards.
Thanks to the ultra-high-speed bus used in UHS-1 (Ultra High-Speed Phase-I) memory cards, data transfer speeds are several times faster. Typically these memory cards can transfer data at 104MB/s. If you want to be sure your memory card supports UHS-1, look for the Roman numeral “I” on the front of the card.

UHS-2 (Ultra High-Speed Phase-II) is a further developed version of UHS-1 and supports data transfer speeds of up to 312MB/s. UHS-2 Cards are usually marked with a Roman numeral “II“.

Although the U1 memory class guarantees a minimum speed of 10MB/s (class U3 — 30MB/s), in practice these cards are almost always much faster. The main thing is that the device in which you use the Ux card should support the UHS standard.
Also worth mentioning is that UHS-I and UHS-II cards are perfectly compatible. It means that you can put the UHS-I card in the UHS-II slot and the UHS-II card in the UHS-I slot.
Memory card file systems
Usually, when you buy a memory card, it is already formatted and has a file system. Standard memory cards are formatted with FAT16, SDHC cards with FAT32, and SDXC cards with exFAT. However, if you want to use any other file system, you can easily format your card with the file system you want, and use the desired partition table.
You can also make the SD card bootable and use it as a recovery tool or to boot the entire system.
You should also be aware that the FAT file system does not support writing files larger than GB. So if you have a memory card with 8 GB or more, you shouldn’t use the FAT file system, but rather format your SD card with NTFS or exFAT.
You can use any available tools to format your SD card — from the system tools to third-party programs. However, the SD Association recommends using the “SD Formatter” utility to avoid deleting the “protected area” which exists on some SD cards with safety features.
Write protection for memory cards
Many standard SD cards have a write-protect switch, the main purpose of which is to prevent writing. Usually, you can find the direction in which to move the slider to activate the write protection on the body of the memory card.

It is also worth noting that not all devices recognize write protection. However, if you are having trouble writing new data to the memory card, the first thing to do is to check if write protection is enabled.
SD express PCIe — the future of SD memory cards
The SD Association recently introduced a new memory card standard, SD 8.0, which uses the PCIe interface for connectivity. By using this connection interface such cards can achieve a minimum write speed of about 4GB/s — four times faster than UHS-II.

Such memory cards will be a great solution for many modern gadgets. For example, more and more smartphones are now getting support for recording video in 8K resolution. The microSD 8.0 standard memory cards will significantly reduce data transfer time.
The main problem with the SD express standard is the slow adoption by device manufacturers and SD card manufacturers. However, as practice shows – this issue soon will be irrelevant, as many giants have already evaluated the full potential of SD express are implementing it in their products.
But what are the advantages of SD Express for the average user?
Faster data write speeds on the memory card mean higher productivity of the device with which this card will work. It will be especially true for small laptops and tablets which have a small amount of memory. After all, today users use microSD cards for such devices, but when working with large files, a decrease in data transfer speeds is honest. SD Express will solve this problem once and for all.
It is also worth noting that manufacturers are planning to increase data transfer speeds to the level of SSD SATA III or even higher.
What should you do if you accidentally format your memory card or lose important data?
Memory cards are a very convenient storage solution because of their size and versatility, so they can be a great solution for transferring data between devices. For example, to transfer photos from your digital camera or smartphone to your notebook, you can simply remove the memory card and insert it into your computer.
However, despite its great convenience, a memory card – like all storage media – cannot keep your data 100% secure. Furthermore, it is not uncommon for users to connect a memory card to their computer and lose data due to viruses, accidental formatting, or data deletion.
Of course, the question immediately arises: what to do next?
Practice shows that the best way to recover your data is not to manipulate the memory card but to use RS Partition Recovery — professional data recovery software.
This program is easy to use and doesn’t require high computer resources, making it a great tool for both PC beginners and PC users with advanced computer skills.
To recover lost data you have:
Step 1. Install and launch the RS Partition Recovery.

All-in-one data recovery software
Step 2. Select the drive or partition from which you want to recover data.
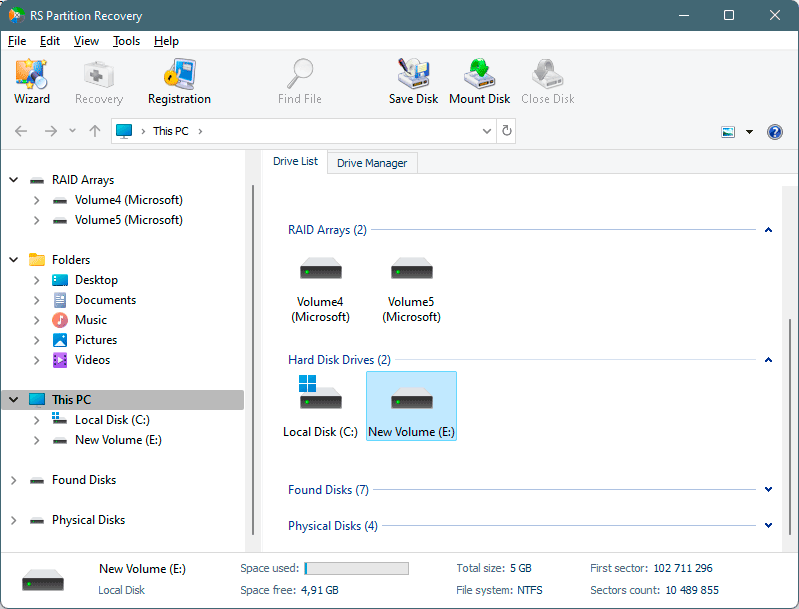
Step 3. Choose the type of analysis.
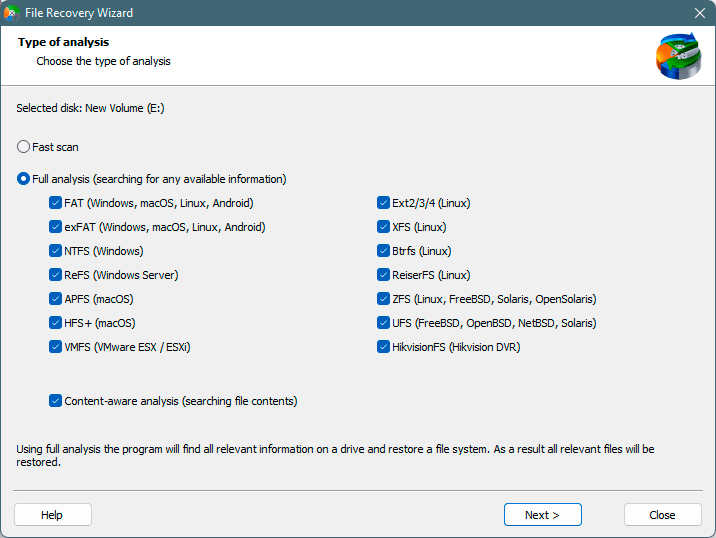
Fast scan you should use in case the file was lost recently. The program will scan the drive quickly and show the files available for recovery.
The Full analysis function allows you to find lost data, after formatting, disc resizing, or file structure corruption (RAW).
Step 4. Preview and select the files to recover it.
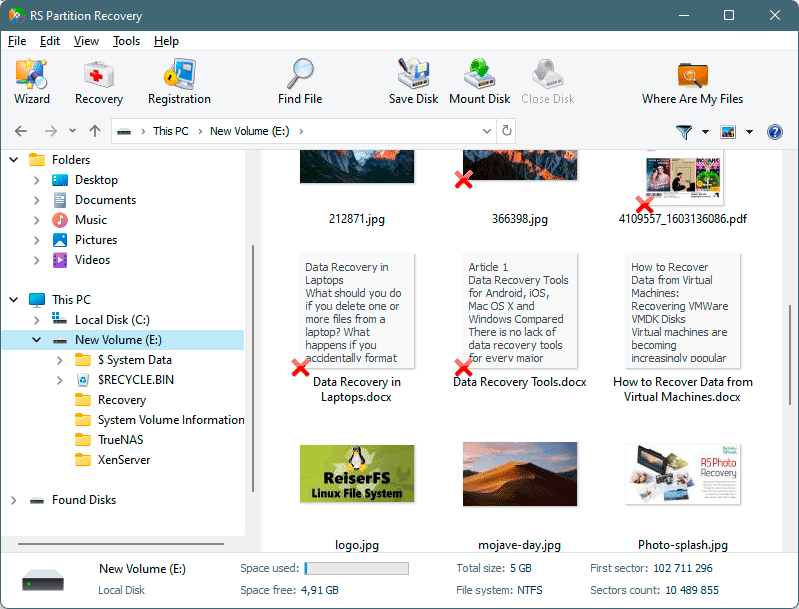
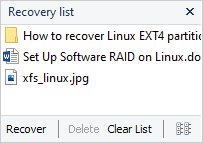
Step 5. Add the files you want to save to the "Restore list" or select the entire partition and click Recovery.
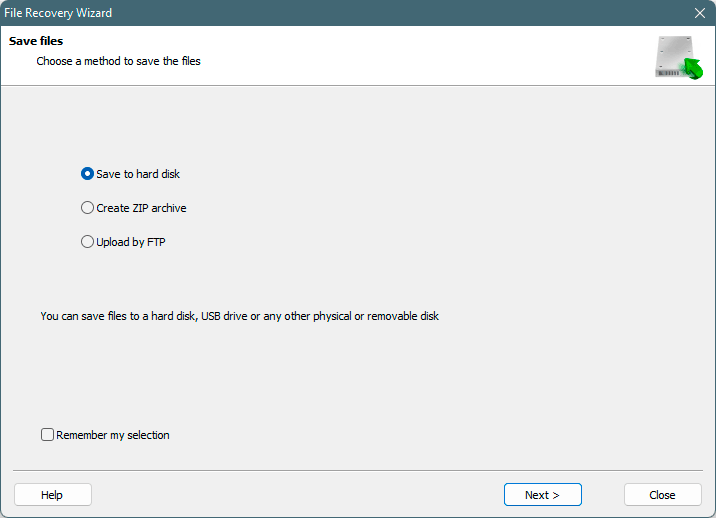
It should be noted that it is best to save the recovered file to an external hard drive or USB flash drive.
After you click “Next“, the recovering process will start. When it finishes, your data will be available again.