If you cannot access data stored on a properly configured computer, receiving errors or having your computer freeze for several seconds (or hang up completely), you may have a problem with the hard drive (assuming you’re not having a virus, that is).
Contents
- Check Your Hard Drives
- Why do hard drives fail?
- Manufacturing Defects Causing Hard Drive Head Crash
- Improper Storage and Usage
- What To Do If You Suspect Your Hard Drive Is About To Fail
- Creating Emergency Backups
- Restoring Emergency Backup
- Conclusion
The best thing you can do under these circumstances is removing the faulty hard drive and attaching it to a different computer. If you still cannot access the same files, you most probably have a problem with the hard drive.
Access problems due to hard drive failure are relatively uncommon; however, they can and do occur on regular basis. The author of this article had no less than five mechanical hard drives fail within the last ten years, making it one hard drive failure every two years.
Check Your Hard Drives
How can you tell the hard drive is about to fail? The symptoms of a failing hard drive can be different. If you hear unusual noises (lout clicking noise, humming or excessive vibrations), the noises may indicate a mechanical malfunction. Check out SMART data of your hard drive with one of the many SMART tools on the market. Can you see the value called “Reallocated sector count”? If it’s value is not zero, and especially if it’s higher than a few sectors, you should start thinking about replacing your drive. If the number grows with the time, you have a problem, and the disk should be replaced as soon as possible.
Why do hard drives fail?
The hard drive is a complex device that has a number of precisely machined moving components inside. These components are controlled by onboard electronics, the hard drive controller. The most common failures are failing (or worn) ball bearings (these are the cause of the loud humming noise and vibrations), read/write head crash (can be observed as loud clicks or scratching noises), premature wear (can be observed as the number of reallocated sectors growing) and motor failure (the hard drive fails to spin up). Head crash is particularly dangerous because it can damage your data by physically scratching disk platters (and this in turn can be observed as a growing number of reallocated sectors).
What are the most common reasons for hard drive head crash? It’s mostly about manufacturing defects, improper storage or usage of the drive.
Manufacturing Defects Causing Hard Drive Head Crash
Manufacturing defects are the most frequent reason of head crash. Some hard drive series (e.g. IBM DTLA, Seagate 7200.10 and many others) were found to have manufacturing defects causing the entire batches of drives to fail quickly within the warranty period. While the manufacturer will typically replace the failed hard drive (sometimes with a refurbished one of the same series), your data can be lost regardless.
Dust particles between platter and head are another common reason of head crash attributed to manufacturing. If air in the assembly room is not clean enough, microscopic dust particles may enter the device during final assembly, causing the drive heads to scratch the platters.
Improper Storage and Usage
When you bought your hard drive, was it shock-proof in the shipping box, or did you just receive the bare device wrapped into a thin layer of anti-static film? Shock caused by accidental dropdown of the drive during storage (or shipping) may cause very slight maladjustments to device’s precise mechanics. These maladjustments will develop into a bigger problem sooner rather than later.
More severe damage may occur if the drive is dropped with its heads not parked.
Another common reason of premature failure is excessive heat inside the drive. Open a SMART monitoring utility and check how hot your hard drives are. If it’s more than about 46C (give or take, depending on the model and rotation speed of your hard drives), your hard drives may need better cooling. This is especially true if your hard drives are operating within a RAID array or are put into a cramped NAS box.
Power outages are yet another common reason for premature hard drive failure.
Finally, operating desktop hard drives under constant server-like load causes both excessive heat and premature wear to head motors. If you are planning to use your hard drives heavily, consider investing in server-grade hardware.
What To Do If You Suspect Your Hard Drive Is About To Fail
If you observe one or more signs of premature hard drive failure, consider replacing the hard drive. However, you may have your data stored on that drive. If you have a habit of maintaining regular backups (including cloud backups via OneDrive, Google Drive, Dropbox etc.), you may not need to worry. If, however, your backup policy was ignorance, you may need professional help.
Creating Emergency Backups
Before trying anything else, make a list of important data stored on your hard drive. Write it down on a piece of paper (your computer may freeze during the backup). Make sure to know the exact locations on the disk where the data is stored. Then, try backing up those files by simply copying them onto another media. If you are able to do that, you won’t need to worry any further. Simply replace the disk with a new one and restore your files.
If, however, you experience a freeze during the backup, you may need to use a dedicated tool for creating an emergency backup. Download and install RS Partition Recovery, preferably onto a USB flash drive. Launch the tool, and use File – Create Virtual Disk Image command to create an emergency backup. When choosing the location of the backup, make sure to specify a different device with sufficient disk space.
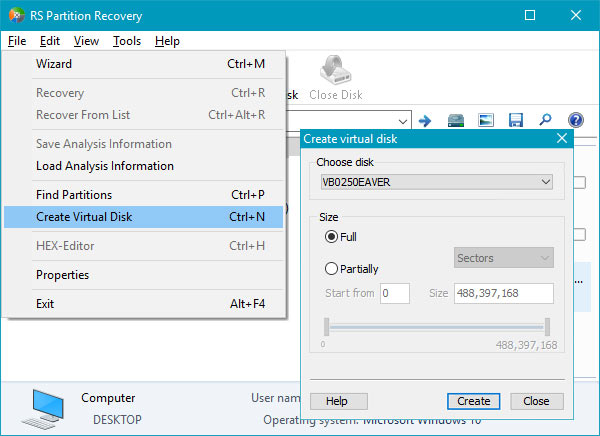
Unlike regular backup tools accessing your disk on file-by-file basis, the point of emergency backup is minimizing the number of head movements in order to reduce the chance of a freeze. Emergency backup will attempt to read your entire disk or partition in one consecutive operation, minimizing the number of head seeks.
As a result, you will get a virtual disk image containing a bit-precise copy of your old hard drive or partition. At this time, you may either disconnect your old hard drive.
Restoring Emergency Backup
After installing the replacement disk, you will need to restore your data. You’ll be using the same tool, RS Partition Recovery, launched from the same location you’ve installed it to. Run the tool, and launch the Recovery Wizard. Choose your newly created Virtual Disk Image as a source. Click Next to scan the disk. You will be presented with a list of files and folders. Select files and folders you’d like to restore, then click Next. You’re almost done: the tool will restore selected data onto your new hard drive.
Conclusion
While there are tools allowing you to act in emergency, it’s best not to have an emergency at all. Open a Dropbox (OneDrive, Google Drive, or Apple iCloud Drive) account. Install a desktop client on your computer. Move your documents (as well as any other important data) into the folder that will be synced with the cloud. Wait till the files are automatically uploaded. Done! From now on, any change you make to synced documents, as well as any files added into the synced folder, will be automatically uploaded into the cloud. When you need to restore, you’ll simply install the cloud client onto your desktop, enter your login and password, and the tool will automatically download your data from the cloud.
Cloud backups are utterly convenient. You won’t need to remember anything but your login and password. Any changes you make to synced files and folders will be backed up automatically and immediately, so you won’t even have to worry about having a recent backup.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can.
One of the reasons may be damage to the file structure of the flash drive.
RS Photo Recovery can recover photos from a damaged memory card.
- Connect the memory card to the computer. The card must be determined.
- Launch RS Photo Recovery and start analysis.
Yes, it is possible. RS Photo Recovery can recover photos from a damaged memory card.
- Connect the memory stick to your computer. The card must be detected.
- Launch RS Photo Recovery software and start the analysis.
This greatly depends on the capacity of your hard drive and your computer's performance. Basically, most of hard disk recovery operations can be performed in about 3-12 hours HDD 1TB in normal conditions.
If the file does not open, it means that the file was damaged or corrupted before recovery.
Use "Preview" to evaluate the quality of the recovered file.
When you try to access the drive, you get the message "Drive is not accessible" or "You need to format the partition drive"
Your disk structure is corrupted.
In most cases, the data may still remain available. Just run the data recovery software and scan the desired partition to get it back.
Please use free versions of programs with which you can analyze the storage and view the files available for recovery.
You can save them after purchasing the program - you won't need to scan it again.
Yes. To work, mount disks in the same way as connecting disk images. Menu: Tools - Mount Disk.