Modern operating systems have many features to enhance data security and usability. In this article, we will compare RAID LVM and RAID mdadm — two interesting technologies whose main purpose is to keep your server, computer, or NAS up, and to save your data in case of hardware failure.

Contents
- What is the difference between Lvm and mdadm
- RAID LVM and RAID mdadm comparison
- Is it possible to use mdadm and LVM at the same time?
- How to recover lost data?
What is the difference between Lvm and mdadm
Lvm and mdadm are two similar and at the same time completely different utilities designed to handle disk information. The similarity lies in the fact that both LVM and mdadm distribute data between drives at the software level. That is, you can create a software RAID array or Lvm disks using only the capabilities of the operating system. No additional hardware is needed. To understand the difference, let us first explain each technology one by one.
LVM (logical volume manager) is an abstract layer between the disk controller and the operating system. In fact, it is a subsystem whereby the user can combine the space of several disks into one volume, and then partition it into several logical disks.
Let’s assume we have two 100 GB disks. Using LVM we can combine them into one 200GB volume (100GB + 100GB) and then create three logical disks: one with 120GB and two with 40GB. In this way, we took a part of the memory of the other drive and joined it to the first one.
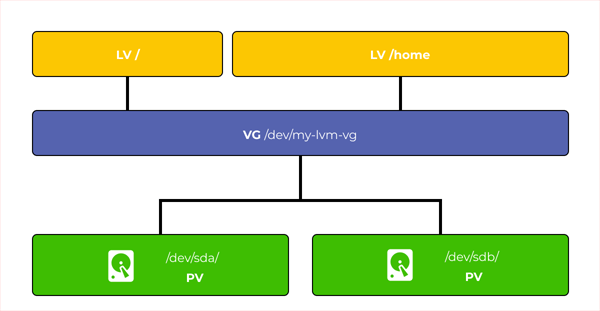
That is, thanks to LVM technology we can distribute memory between the disks without being limited by the size of any of the drives. The only limitation will be the amount of memory shared by all disks.
Furthermore, LVM allows you to dynamically add new disks to increase the available memory, flexibly manage disks at the physical level (add disks without stopping the server, NAS, or computer), and change disks by stopping the storage only for the time of physical disk replacement (without having to stop while adding disk in the software level). Agree, LVM is a very handy feature. However, LVM does not provide any redundancy.
Yes, LVM can implement some semblance of a RAID array using its solutions, but they will either be severely inferior in performance or will pass commands to the md utility, i.e. the mdraid device itself. But, we will talk about this a bit later.
Let’s talk about what mdadm is.
Mdadm is a special Linux operating system utility whose main purpose is to create and manage RAID arrays. That is, the main purpose of mdadm is to provide redundancy, which means to save the data if one or more disks fail (depending on the RAID type selected). In fact, mdadm communicates with disks and distributes data between them on a physical level, having absolutely nothing to do with the logical partitioning of disks. The entire RAID array of several disks is displayed in the operating system as a separate disk drive which can be manipulated in the same way as a regular disk drive.
RAID LVM and RAID mdadm comparison
As mentioned above – it is possible to create software RAID using LVM technology (for example, LVM RAID 0 or LVM RAID 5).
LVM RAID refers to a special method of building an LV partition that uses a DM (Device Mapper) driver to manage LV partitions and an MD driver to distribute information between the disks.
LVM RAID can also be created by bypassing the MD driver, but in this case, the performance of such an array will suffer greatly. Moreover, if something happens to any of the disks – its replacement and data recovery will be very difficult.
So, so far everything seems clear. Now let’s talk about the disadvantages of this solution.
Firstly, it is worth mentioning that when working with standard LVM volumes, you have to know a very large number of commands and utilities to be able to work correctly with the volumes, as there is no graphical shell.
Secondly, when working with LVM, it is important to know which filesystems to use (i.e. those that are scalable) and which are not. Your choice of the filesystem has implications for adding new disks.
In short, LVM is quite complex to maintain and requires the user to have a thorough knowledge of the operating system.
It is worth mentioning that the Windows and Mac OS operating system does not support working with LVM.
The other disadvantage of LVM comes up when using it on SSDs. To understand this, let’s discover how LVM works.
All information in LVM is divided into extents (these are blocks of information) which are written to disk. The minimum size of an extent is 4 MB. There are quite a few algorithms to write extents to disks. We will take the simplest one, called linear, as it is the easiest way to understand how LVM works.
When using the linear algorithm, all extents are written to the disks in order. If there is not enough disk space to write the extents, they are written in order to the second one, and so on.
That is, physically the file may be stored on several disks at the same time, but LVM subsystem remembers the order of the extents and thus knows in what order to read them to open the desired file. Schematically, it can be shown as follows:
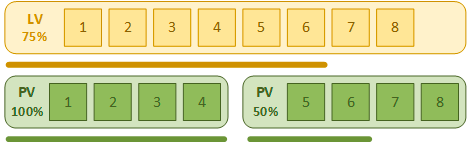
However, this is a disadvantage of LVM – since all extents are written sequentially – recording to the next SSD drive will start only after the first one is completely full. As you know, it is not recommended to fill SSD drives, because it severely degrades performance and reduces the performance of the garbage collector (in other words, it reduces the speed and reduces the lifetime of the drive).
And here many will say that you can use striping method (some analogue of RAID 0 in mdadm). They will be partially right, as the load on the disks will decrease and the read/write speed will increase in direct proportion to the number of used disks, since the information will be written to all disks simultaneously. However, there are also pitfalls here…
The thing is that to expand our volume we will have to use a multiple of the number of disks already in use. That is, if we used 3 disks, then we can add 3, 6, 9, etc. disks.
But the most important thing is that when adding a new group of disks, the striping will not be done between all disks at the same time, but within each disk group.
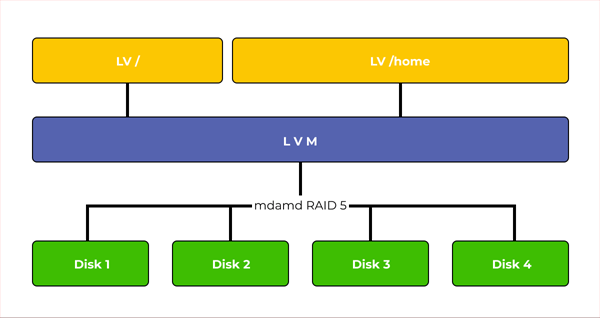
It turns out that recording to a new group of disks will begin only when the first one is full. Hence the conclusion that the first disk group will work under stress.
Mdadm can solve this problem, since its new versions allow adding new disks to the RAID 0 array without any problems, after which writing to them will stripe with the previously installed disks, reducing the load and wear level for SSD drives.
In fact, mdadm is a highly functional utility that adds RAID support to Linux at the kernel level (that is why LVM uses the MD driver to work with disks at the physical level).
There is also a graphical shell for mdadm called “Webmin” which means that the user can create a software RAID array of almost any type in just a few clicks (including RAID 10, 50, 60), rather than using a bunch of commands, etc. (effectively requiring no special knowledge of the operating system). You can read about how to do this in the article “How to create a software RAID?“
It is also worth noting that RAID arrays created with the mdadm utility have the highest performance as they do not have any “middlemen” in the form of additional drivers and utilities to send commands to the drives. It is also the reason why a failed disk can be replaced more quickly than with LVM RAID, as no extra manipulation of the LVM subsystem is needed.
For this reason we recommend that you use mdadm to create a software RAID, since it will be both faster and more reliable.
Summarizing all of the above, the following conclusion can be made:
The advantages of LVM:
- flexible allocation of disk space;
- dynamic disk addition (without stopping the server);
The disadvantages of LVM:
- complexity of administration (requires knowing a large number of commands and utilities);
- it is very difficult to replace the disks in a RAID array;
- arrays created with LVM will be slower;
- it is not recommended to use them on SSD drives;
- it is necessary to know which file systems can be used and which are undesirable;
- many operating systems do not support LVM;
The advantages of mdadm:
- maximal fast RAID arrays;
- dynamic drive addition to the RAID array (using hot spare disks);
- quick and easy failed disks replacement;
- easy administration (thanks to the graphical shell Webmin);
The disadvantages of mdadm:
- the user cannot flexibly allocate disk space (actually limited by the volume of disks and the type of RAID used);
Based on the above, you can choose which technology best meets your needs, but what if you want both the reliability of RAID arraysand the flexibility of LVM volumes?
There is an answer to this question and it is described in detail in the next paragraph of this article.
Is it possible to use mdadm and LVM at the same time?
We have already said that the best way to create RAID arrays is with the mdadm utility. However, if you want to have the flexibility to create volumes as well as the reliability, you can use LVM over RAID. That is, first you create a RAID of the required type (e.g. RAID 5) and then use LVM to create several logical drives.
It will provide reliability and speed, plus you can partition the disk space however you want. Moreover, if you ever need to add a new disk to the system, you can do it with mdadm.

The disadvantage is that you have to know a lot of commands to work correctly with LVM volumes because although you can create a RAID array in a few clicks with Webmin, LVM is still difficult to administer and there is nothing you can do about it.
Important note: If you decide to use RAID in combination with LVM you have to do RAID first and build the LVM volumes over it. If you do the opposite, you will get very difficult to manage the array which is also not very fast. And if any of the disks fail, it will be very difficult to replace them.
How to recover lost data?
Despite the use of various technologies, such as RAID arrays, no one can guarantee 100% data security. And if the use of RAID arrays allows to somewhat increase the level of data safety, different kinds of add-ons, such as LVM, can cause the loss of important data instead of adding new functionality. Furthermore, although LVM offers some resemblance to RAID, it is less reliable than mdadm RAID.
But even this technology can not give a 100% guarantee that you will not lose information, because there are controller failures, and the accidental data deletion or accidental array formatting can not be excluded.
That’s why the user must know what to do if he loses the important information for any reason. In such a situation one should immediately use a professional RAID reconstructor which will be able to provide successful data recovery of the RAID array.
We suggest using RS RAID Retrieve – the best solution for reassembling a broken RAID array and further lost data recovery.
The program is simple and easy to use and supports virtually all RAID (including hybrid) and LVM configurations. In addition, RS RAID Retrieve supports ALL modern file systems, as well as NAS storage. It also allows you to recover data from RAID arrays no matter what operating system they were running on – be it Windows, Linux, MacOS, or Solaris.
Just connect all the disks of the array to a running computer and follow a series of simple steps:
Step 1: Download and install RS RAID Retrieve. Launch the application after installing. The built-in “RAID constructor” will open in front of you. Click “Next“
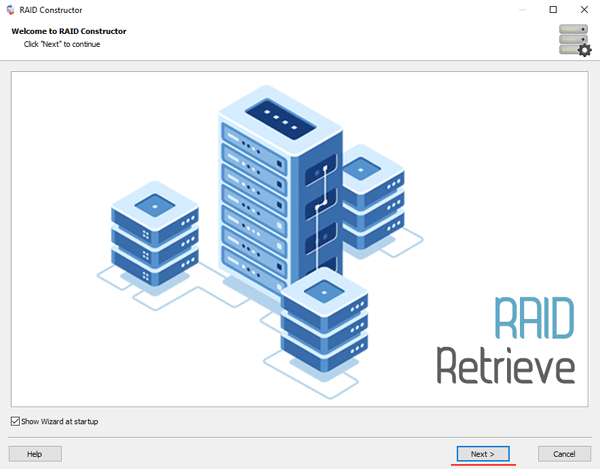
Step 2: Choose the method of adding a RAID array for scanning. RS RAID Retrieve offers three options to choose from:
- Automatic mode – allows you to simply specify the drives that made up the array, and the program will automatically determine their order, array type, and other parameters;
- Search by manufacturer – this option should be chosen if you know the manufacturer of your RAID controller. This option is also automatic and does not require any knowledge about the RAID array structure. Having the manufacturer’s information allows you to reduce the time to build the array, and is, therefore, faster than the previous option;
- Manual creation – this option is worth using if you know what type of RAID you are using. In this case, you can specify all parameters you know, and those which you do not know – the program will automatically determine
After you select the appropriate option – click “Next“.
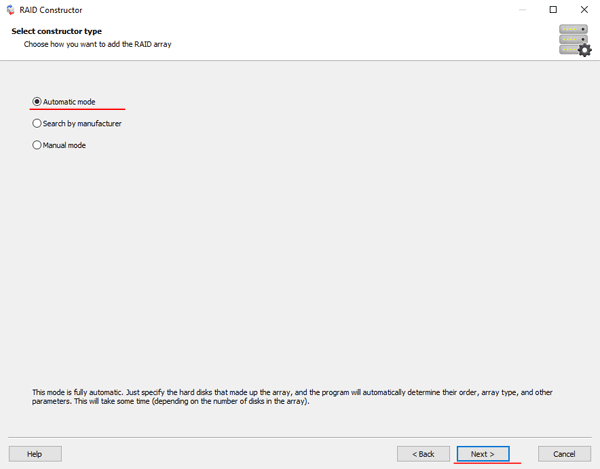
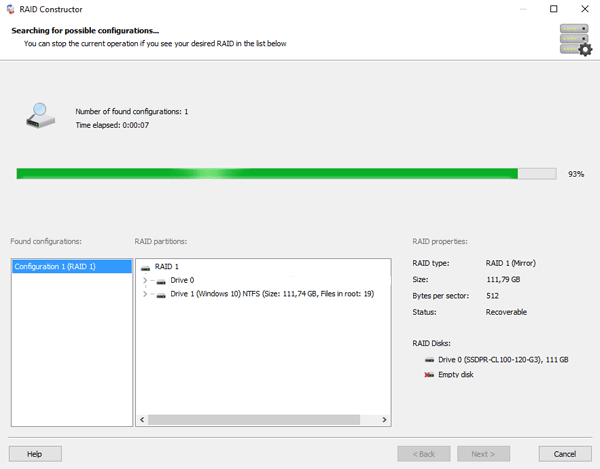
Step 3: Select the disks that make up the RAID array and click “Next“. It will start the process of detecting the array configurations. When it is complete, click “Finish“.
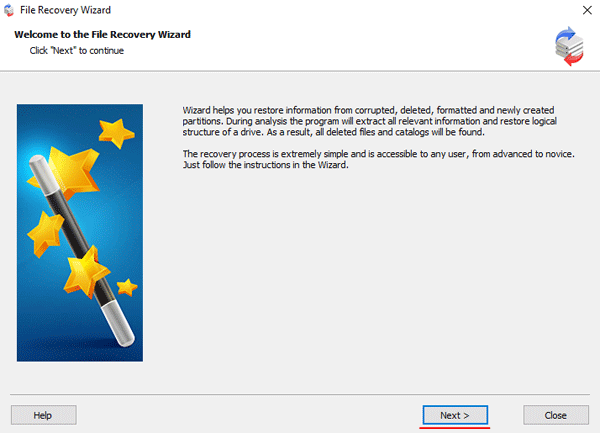
Step 4: After the constructor builds the array – it will appear as a regular drive. Double left-click on it. The File Recovery Wizard will open in front of you. Click “Next“
Step 5: RS RAID Retrieve will offer to scan your array for files to recover. You will have two options: a quick scan and a full analysis of the array. Select the desired option. Then select the file system type that was used on the array. If you do not know this information, check all available options, like on the screenshot. It is worth noting that RS RAID Retrieve supports ALL modern file systems.
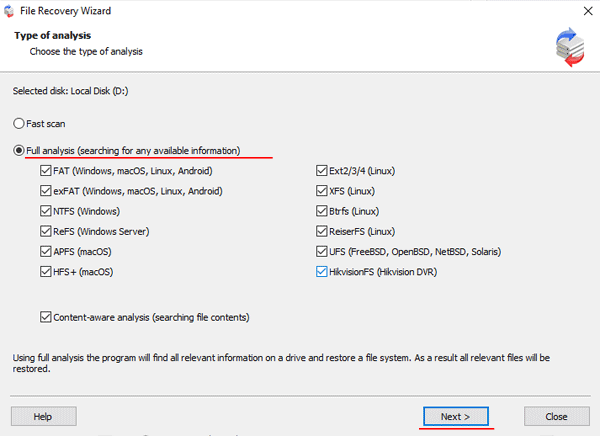
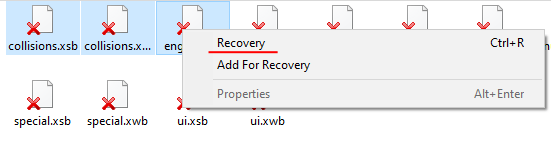
Step 6: The array scanning process will start. When it finishes, you will see the previous structure of files and folders. Find the necessary files, right-click on them and select “Recovery“
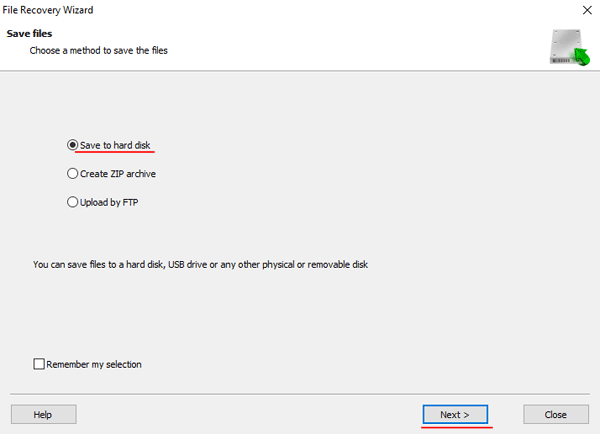
Step 7: Specify the location where the recovered files will be saved. This can be a hard drive, a ZIP-archive, or an FTP-server. Click “Next“
After clicking the “Next” button, the program will begin the recovery process. When it finishes – the selected files will be in the specified location.
After all, files are successfully restored – recreate your RAID array, and then copy the files back.
As you can see, the RAID data recovery process is quite simple and doesn’t require much PC knowledge, making RS RAID Retrieve the perfect application for professionals and novice users alike.