Multi-drive arrays in RAID5 configuration provide an excellent balance of performance, security, and price, so they are often the user’s choice. What are the features of this RAID level? What problems are specific to RAID5? How to deal with unexpected situations? How to recover data from RAID 5 or the entire array if it is damaged?
Contents
- RAID5: what's the point
- Advantages and disadvantages of this RAID5 level
- Why RAID-5 arrays fails?
- How to recover RAID 5?
RAID5: what’s the point
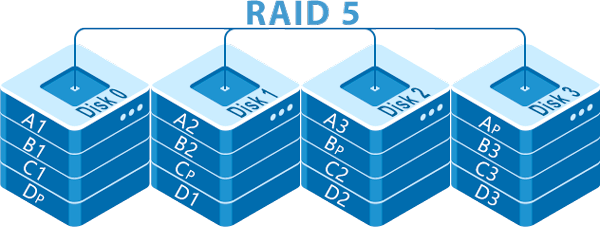
RAID5 can be built with at least three disks. An additional disk is needed to implement the parity checksum algorithm. Both regular files and parity data are not stored on a separate HDD as in RAID3, but in blocks spread across all disks. It allows for increased efficiency and disk space efficiency compared to RAID3 and RAID4.
The “usable” volume of a RAID 5 array is equal to the total volume of its disks excluding one drive. Parity checksums stored on disk spaces equal to the capacity of that drive are used to recover lost data if one of the drives fails. Since all data is additionally duplicated on other drives, the controller calculates the missing blocks by itself and the array continues to work as usual.
RAID5 can be implemented in software, but it is recommended to use a hardware controller. For better write performance an additional cache is installed on it. The safe, efficient storages in this configuration are perfect for creating file servers.
Advantages and disadvantages of this RAID5 level
The already mentioned advantage of RAID5 is good disk space efficiency. Only one drive of the system is not used directly for data storage and processing. The system also has several other advantages:
- Rather high data transfer rate. The highest speed will be for data reading procedures. For write procedures, it is somewhat lower because of the need to calculate parity.
- The configuration redundancy guarantees the safety of all data if one of the drives fails. Access to the information is preserved even after replacing the faulty disk: the controller just overwrites the recovered blocks to a new disk.
The disadvantage of the Five level is a lower performance than that of RAID0, which, however, is compensated by the security characteristics of the system. Additional problems can appear after one of the disks fails, which automatically reduces the redundancy of the system to the stripe level, i.e. to level 0:
- Drive failures affect system throughput
- Recovering and transferring information to a new disk, especially when working with large amounts of data, takes a long time, and the loading on the affected array increases, and with it the likelihood of another drive failure.
- Destruction of the second disk before the first disk has been fully recovered leads to complete array destruction.
Why RAID-5 arrays fails?
Sometimes after a failure on one of the disks, the controller misconfigures the system and the RAID stops working correctly, and sometimes even crashes completely. Problems can also occur during the rebuild phase after replacing a hard drive.
However, even if RAID5 does not detect any obvious problems after the disk failure, an unreasonable decrease in array performance should be alerting. In such cases, quick replacement of the problematic drive will prevent difficult situations and a possible crash later on.
As long as the number of defective media does not exceed the RAID5 fault-tolerance threshold even a failed array can be rebuilt programmatically – just like the simplest RAID0. If faults are found on two or more disks, you will have to restore them to working condition first, or at least remove all data from them by creating an image. Only after that you can begin to build the array.
Among the typical and most probable causes of RAID5 failures we will name the following:
- controller failure or malfunctions;
- errors occurring while rebuilding RAID 5 or formatting its partitions;
- massive failures or errors on the array disks, including the appearance of bad blocks;
- power surges or electronic damage;
- virus infection;
- unexpected configuration changes or parity problems;
- access problems after a hardware upgrade.
Of course, like any technique, all components of multidrive arrays are also subject to common mechanical failures due to falls, overheating, contact with water, damaged cables and cables.
Separately highlight the causes of malfunctioning due to human error. Sometimes wrong actions are taken in an attempt to fix the problematic RAID, but often it only leads to new complications. What exactly RAID 5 owners do “sin”:
- Accidental deletion of files or partitions;
- User initializing the array;
- Incorrect array building, including rearranging the drives;
- improper rebuild and other operations without additional data protection;
- running checkdisk, fsck after an incorrect rebuild;
- copying, changing files, saving new data to recoverable drives;
- formatting or relocation of partitions, reinstalling the operating system as an attempt to restart the problematic disk.
None of these actions are needed to recover data from RAID 5 for minor malfunctions. For serious problems, any of these will only harm. So what is the right thing to do to safely retrieve the information from the array?
How to recover RAID 5?
Data recovery from RAID 5 is almost always possible, and modern RAID recovery software allows you to do it even at home – specialist participation is now required only in exceptional cases. Nevertheless, the right sequence of actions is important for a successful recovery.
First, try not to do anything until you have backed up the damaged and working disks. All further actions can be performed directly with the copy. Otherwise, every operation in the recovery process may cause additional damage.
Note that if the array is “healthy” and you only need to recover a few deleted files, there is no need to send the entire RAID to be recovered.
Secondly, always make sure you have backed up any important data before starting a RAID 5 rebuild: if two or more disks are damaged it is a must and it is important to keep the most valuable data on the disk images at least.
So, to start recovering data from RAID 5, reconstructing the array system, repairing its structure and solving other issues with the problematic array, download the program RS RAID Retrieve.
Data recovery from damaged RAID arrays
Important: Remember that no new data can be saved on the drive to be restored. Both the program and all files and data blocks that you recover using it, save on separate drive
Option №1. “Lucky”
Your hard drives are working and connected in the correct order.
RS RAID Retrieve can work with hard drive images which can be used to restore the raid configuration and retrieve information.
After you start RS RAID Retrieve, the program will automatically search for raid configurations on the connected hard drives or added images.
The found arrays will be added to the program window.
To extract information from the found array it is enough to run a quick analysis, based on the results of which – to save the data.
Option №2. Rebuilding RAID5 when two of the five hard disks fail.
The RAID 5 array uses a parity distribution of blocks of information across the entire array space. If one drive out of five fails, RAID5 will continue to work, but the array will be much slower.
If two or more disks out of five for RAID5 fail, further operation will not be possible.
To retrieve information from the remaining working drives, connect them to your computer or create images and add them to RS RAID Retrieve. If you do not know which disks are working, connect them all, but it is better to create images.
If the program cannot automatically detect the raid configuration when it starts, you need to run.
In the Raid type field we set, in our case, RAID5 (Pariry).
Specify the known data used when creating the array, such as: block order and size, parity delay, number of bytes per sector (512, 4096) and byte order
If you don’t have any data, leave the checkbox on “define automatically”. However, specifying as many additional parameters as possible will reduce analysis time and reduce the number of possible RAID configurations.
Add disks or mounted images of those disks.
In our case, add the remaining three working disks of the five that were used to create the array.
Non-working drives are filled with “+” Empty drives.
Use the arrows to set the correct disk order.
The previous result of the array configuration will be immediately displayed in the window.
When the configuration is selected, add it to the main program window for further analysis.
If the exact parameters were not specified, the program prompts you to add several configurations for analysis.
To recover information from a RAID, start the Recovery Wizard
Once the analysis is complete, check how the data has been recovered.
A full analysis will be able to find more files to save without damage.